[AUG. 2024] “Degenerative Arthritis” Robotic Joint Replacement Surgery at LeeChunTek Hospital
- Name 관리자
- Date 2024-08-19
Common “Degenerative Arthritis” in an Aging Society
Treated with Robotic Joint Replacement Surgery at LeeChunTek Hospital!
- Over 17,000 Successful Cases in 20 Years Since
the First Robot Introduction in Korea -
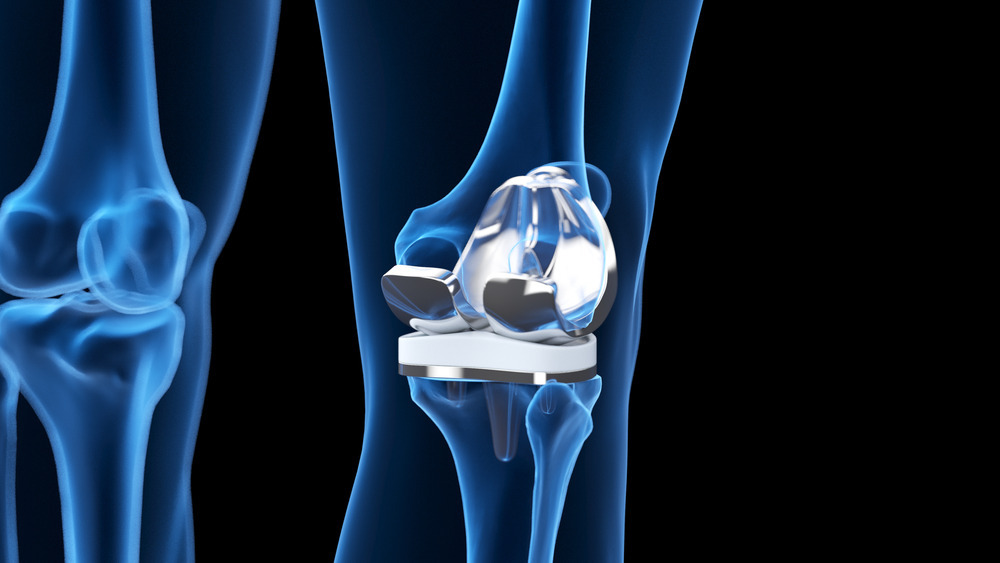
South Korea has begun to enter an ultra-aged society, with the population aged 65 and older surpassing 10 million. It is also reported that 80% of this age group suffers from degenerative arthritis, a common age-related disease.
Degenerative arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation and pain due to the wear and tear of joint cartilage, most commonly occurring in the knees. Major risk factors include being female, age, overweight, overuse, and genetic factors. The severity of joint damage is classified into four stages, from 1 to 4.
In the early stages, conservative treatments such as medication, injection therapy, and physical therapy can help reduce pain. If the pain worsens, options like intra-articular steroid injections or cartilage injections may be considered. In the advanced stages, if pain makes walking difficult, surgery should be considered. When deciding on surgery, factors such as age, pain level, and the extent of joint damage should be considered. For relatively younger patients, procedures like proximal tibial osteotomy or partial knee replacement may be performed, while older patients may undergo total knee replacement.
The most crucial aspect of joint replacement surgery is the alignment of the lower limbs. The thigh and ankle must be perfectly aligned in a straight line, but there is a possibility of error when performed by human hands. Since the shape of the knee and the degree of bone deformity vary from person to person, traditional knee surgeries relied heavily on the surgeon's experience and skill, making it difficult to customize the surgery to individual characteristics. Orthopedic specialist Soo-hyun LEE at LeeChunTek Orthopedic Specialty Hospital, stated, “In joint replacement surgery, proper alignment from the thigh to the ankle is essential for the longevity of the artificial joint. However, when performed manually, there is a high chance of error in this angle. This is where robotic joint replacement surgery comes into the spotlight.” Robotic joint replacement surgery inputs the patient’s bone information obtained from a 3D CT scan into a computer, allowing for virtual surgical planning tailored to the individual’s characteristics. Based on this plan, a special robot performs the bone cutting, enabling customized joint replacement surgery. This method offers advantages such as less pain, faster recovery, and a longer lifespan for the artificial joint.
Orthopedic specialist Soo-hyun LEE stated, “As we approach an ultra-aged society, it is crucial to manage degenerative arthritis to prevent a decline in quality of life.” He emphasized the importance of avoiding activities that put strain on the joints to prevent further damage. “If the joints are already damaged, it is essential to actively seek various treatment options to ensure that we can use our joints for as long as possible.”
Meanwhile, LeeChunTek Hospital introduced the advanced surgical robot “Robodoc” in 2002, becoming the first in the country to do so, and has been performing surgeries for over 20 years. Recently, the hospital developed its own robotic system for joint replacement surgery, called Dr. LCT, and has conducted approximately 17,000 robotic surgeries to date.
Website: https://www.lct.co.kr/en/